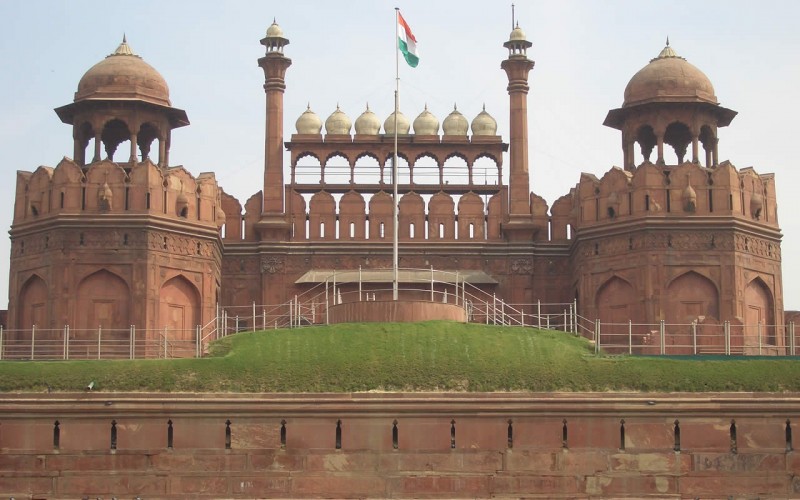
Red fort
In 1638 Shahjahan transferred his capital from Agra to Delhi and laid the foundations of Shahjahanabad, the seventh city of Delhi. It is enclosed by a rubble stone wall, with bastions, gates and wickets at intervals. Of its fourteen gates, the important ones are the Mori, Lahori, Ajmeri, Turkman, Kashmiri and Delhi gates, some of which have already been demolished. His famous citadel, the Lal-Qila, or the Red Fort, lying at the town’s northern end on the right bank or the Yamuna and south of Salimgarh, was begun in 1639 and completed after nine years. The Red Fort is different from the Agra fort and is better planned, because at its back lies the experience gained by Shahjahan at Agra, and because it was the work of one hand. It is an irregular octagon, with two long sides on the east and west, and with two main gates, one on the west and the other on the south, called Lahori and Delhi gates respectively. While the walls, gates and a few other structures in the fort are constructed of red sandstone, marble has been largely used in the palaces.
From the western gateway after passing through the vaulted arcade, called Chhatta-Chowk, one reaches the Naubat- or Naqqar-Khana (‘Drum-house’), where ceremonial music was played and which also served as the entrance to the Diwan-i-‘Am. Its upper storey is now occupied by the Indian War Memorial Museum.
The Diwan-i-‘ Am (‘Hall of Public Audience’) is a rectangular hall, three aisle deep, with a façade of nine arches. At the back of the hall is an alcove, where the royal throne stood under a marble canopy, with an inlaid marble dias below it for the prime minister. The wall behind the throne is ornamented with beautiful panels of pietra dura work, said to have been executed by Austin de Bordeaux, a Florentine artist. Orpheus with his lute is represented in one of the panels here. Originally there were six marble palaces along the eastern water front. Behind the Diwan-i-‘ Am but separated by a court is the Rang-Mahal (‘Painted Palace’), so called owing to coloured decoration on its interior. It consists of a main hall with an arched front, with vaulted chambers on either end. A water-channel, called the Nahr-i-Bihisht (‘Stream of Paradise’), ran down through it, with a central marble basin fitted with an ivory fountain. The Mumtaz-Mahal, originally an important apartment in the imperial seraglio, now houses the Delhi Fort Museum.
The Diwan-i-Khass (‘Hall of Private Audience’) is a highly-ornamented pillared hall, with a flat ceiling supported on engrailed arches. The lower portion of its piers is ornamented with floral pietra dura panels, while the upper portion was originally gilded and painted. Its marble dias is said to have supported the famous Peacock Throne, carried away by the Persian invader Nadir Shah.
The Tasbih-Khana (‘chamber for counting beads for private prayers’) consists of three rooms, behind which is the Khwabgah (‘sleeping-chamber’). On the northern screen of the former is a representation of the Scales of Justice, which are suspended over a crescent amidst stars and clouds. Adjoining the eastern wall of the Khwabgah is the octagonal Muthamman-Burj, from where the emperor appeared before his subjects every morning. A small balcony, which projects from the Burj, was added here in 1808 by Akbar Shah II, and it was from this balcony that King George V and Queen Mary appeared before the people of Delhi in December 1911.
The Hammam (‘Bath’) consists of three main apartments divided by corridors. The entire interior, including the floor, is built of marble and inlaid with coloured stones. The baths were provided with ‘hot and cold water’, and it is said that one of the fountains in the easternmost apartment emitted rose water. To the west of the Hammam is the Moti-Masjid (‘Pearl Mosque’), added later by Aurangzeb. The Hayat-Bakhsh-Bagh (‘Life-giving garden’), with its pavilions, lies to the north of the mosque, and was later considerably altered and reconstructed. The red-stone pavilion in the middle of the tank in the centre of the Hayat-Bakhsh-Bagh is called Zafar-Mahal and was built by Bahadur Shah II in about 1842.
In 1644, Shahjahan commenced in Delhi his great mosque, the Jami’- Masjid the largest mosque in India, and completed it in 1650. Its square quadrangle with arched cloisters on the sides and a tank in the centre is 100 m. wide. Built on a raised plinth, it has three imposing gateways approached by long flights of steps. Its prayer-hall, with a facade of eleven arches, flanked by a four-storeyed minaret on either end, is covered by three large domes ornamented with alternating stripes of ‘black and white marble.
Entrance Fee:
Citizens of India and visitors of SAARC (Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Maldives and Afghanistan) and BIMSTEC Countries (Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka, Thailand and Myanmar) – Rs.10 per head.
Others:
Rs. 250/- per head (Free entry to children up to 15 years)